Last spring, I took a class on social psychology. It was one of the most useful classes I’ve ever taken, so I figured I’d share some of the more interesting findings. Each paragraph has a citation to its right so you can get more information or read the original study.
1. Reciprocity has a strong effect on us.
20% of people send Christmas cards back to people they’ve never met, just because they received one from them. For the same reason, tips to waiters go up 3.3% when an after-dinner mint is provided with the receipt. And when the server looked the diner in the eye and gave them a second mint? Tips went up 20%.
2. You attribute a higher value to things you already own—this is known as the endowment effect.
Willingness to sell was twice as high as willingness to pay in one study. In other words, participants were willing to buy a mug for $5, but once they owned it, they wouldn’t sell for less than $10.
3. Heat makes us angry, and sadness physically makes us colder.
When you feel rejected, you report the room as being colder and you prefer warmer foods over colder foods. Crime rates are higher in hotter regions, and crime is more likely on warmer days. Baseball pitchers are more likely to hit batters when it’s hot. This occurs because heat causes arousal, but people misattribute that arousal to situations around them and not to the heat.
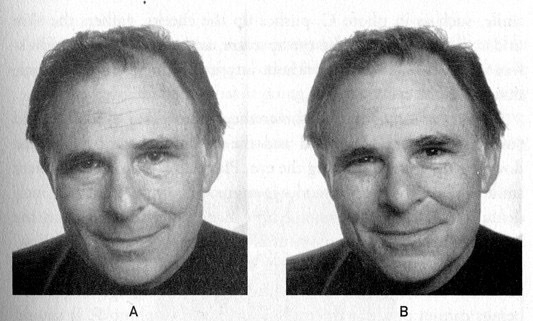
Duchenne smiles (example B) that are exhibited in high school yearbook photos are correlated with better life outcomes 30 years later. Here, Paul Ekman—an expert in facial psychology—exhibits both non-Duchenne (exhibit A) and Duchenne smiles.
4. Smiling is contagious—and can predict your happiness, professional success, and lifespan.
Humans laugh more at movies when other people laugh. Additionally, many people smile at getting a strike in bowling only after they turn around to their friends—you smile for the social approval, not for doing something successfully. In another study, students who exhibited “Duchenne smiles”—a more authentic type of smile that engages the eye and mouth muscles—in their high school yearbook were more likely to get married and were more likely to self-describe as “happy” 30 years later. Students with less intense smiles were more likely to be divorced. And in any given year, people who exhibited Duchenne smiles in their high school yearbook were half as likely to die.
5. How we’re approached and our desire to be consistent affect our decisions.
If I asked you to volunteer for an “Experiment at 7AM,” would you do it? What about a “7AM experiment”? 56% of people asked to volunteer for the first did so, but only 24% volunteered for a “7AM experiment”—fewer people want to wake up early, so the ordering of the words matters. In another experiment, some participants were called and asked if they would hypothetically volunteer for the American Cancer Society. When they were contacted a few days later and asked to volunteer, 31% agreed—versus 4% of people who were cold-called and asked to volunteer for the first time.
6. We act differently when reminded of who we are.
When participants were told that men and women scored differently on a particular test, female participants’ performance dropped dramatically. Male participants’ performance on a task dropped after interacting with an attractive female participant. When children are in a group on Halloween, they take more candy on average—but when children were singled out and asked their names, they took far less candy.
7. Being watched sometimes helps—except when eating.
Having an audience of people watching you complete a task improves performance on simple tasks but hinders performance on more complex tasks or when learning a new skill (they showed this with both humans and cockroaches—don’t ask). The mere presence of someone in the room causes this effect; even a repairman working on something in the corner slowed people down. Yet when it comes to eating, a full chicken will overeat in the presence of another chicken, and animals eat more in pairs than when alone.
8. Comparing people to their friends is the most effective way to make them do something.
When an electric company tried to encourage people to save energy at home, telling them “your neighbors are reducing their energy use” led to a 2% reduction in household usage. Telling people “save energy to save money” or “save energy to save the environment” did not decrease, and in some cases increased, energy usage.
9. Context—where we do something—has a substantive effect on what we do.
56% of actual voters voted for a pro-school budget when voting in a school vs. 53% otherwise. While that effect may not seem huge, it’s statistically significant and was reproduced in a lab environment (64% of people voted for a fake pro-school budget when shown pictures of a school vs. 56% who voted for it otherwise).
10. The more you’re exposed to something, the more you like it—this is called the mere exposure effect, and it works in milliseconds.
Participants shown a foreign word frequently were more likely to say the word had a positive connotation. The most immediate application of this effect is advertising; the more often you’re exposed to a commercial or ad, the more positively you will rate the company. Flashing images that elicit positive or negative emotions for only a few milliseconds subliminally conditions your attitude.
People liked familiar objects more than abstract patterns, but in both cases participants overwhelmingly preferred curved objects over objects with sharp edges. Objects in category C (featuring both curves and edges) fell in between.
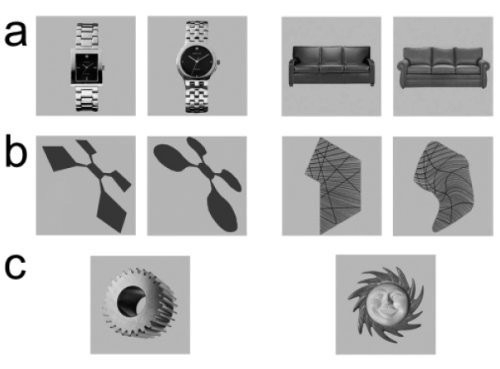
11. Curves > Edges.
Humans overwhelmingly prefer curved visual objects over objects with jagged lines.
12. Don’t get hurt when there are a lot of people around you.
Bystanders are less likely to intervene in a crime or help in an emergency as the number of observers increases, as each individual feels that someone else will help and responsibility is diffused. When a victim is bloody, people help less often—likely because there is a chance they would be exposed to pathogens. But victims who scream receive more help than those who don’t—clear and unambiguous danger is helped far more often than not.
13. We really want to be happy, but being too happy can negatively affect our work.
In a study of 10,000 participants from 48 different countries, happiness is rated as more important than any other personal outcome—more than finding meaning in life, becoming rich, or getting into heaven. Happy people more often label themselves as “curious,” and depressed people are more likely to notice small changes in facial expressions. Yet extremely happy people (9/10 or 10/10 on a happy scale) got worse grades and had lower salaries than moderately happy people (6/10, 7/10, or 8/10 on a happy scale).
14. We do stupid things because we want to conform.
In one study, a participant was placed in a group and asked to answer a seemingly simple question. The rest of the people in the group were all told to respond with the same incorrect answer to the question, after which the participant was asked to answer in front of the group. 37 of 50 participants gave the same incorrect answer as the rest of the group (even though it was very clearly wrong), either because they wanted to be “liked” by the group or because they thought the rest of the group was more informed than they. This effect was dampened by having just one other person in the group agree with the participant.
15. We have trouble separating out traits in a person.
Globally positive or negative reactions on a person (“he’s a nice guy”) affect our judgment of a person’s specific traits (“he’s attractive”). This is called the halo effect, and is particularly noticeable in celebrities; their attractiveness or fame also leads us to believe they’re intelligent, happy, or honest.
16. We’re influenced by very particular types of rewards.
Expected rewards reduce motivation on a task. Surprise rewards increase motivation on the same task. Fixed rewards are less powerful than performance-based rewards, even with creative tasks.
17. Authority can fundamentally change our emotions and behavior.
In the Stanford Prison experiment, participants were split into prisoners and guards and placed into a mock prison. In just six days (of a planned two weeks), the experiment had to be shut down because guards were harassing and abusing prisoners, and prisoners began showing signs of emotional breakdown.
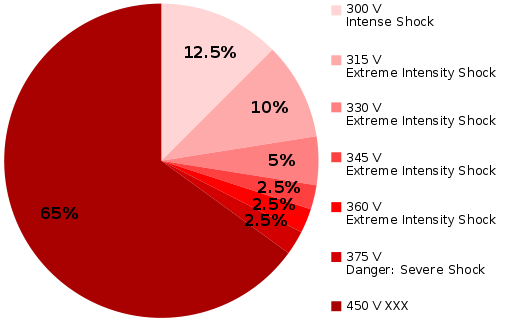
65% of participants knowingly delivered a lethal dose of electricity to a participant (who they later learned was fake) simply because the instructor in the room told them to.
18. Authority can also make us be obedient and do things to other people we could never imagine.
In the famous Milgram experiment, participants were told to administer a shock of increasing strength when a participant in another room gave incorrect answers to a series of questions. About halfway through, the shocks were labeled “danger: severe shock” and a recording was played begging the experimenter to stop the experiment. Yet in 63% of cases, the participant administered the maximum shock, even when the person they thought they were administering a lethal dose of electric shock to another human being.
A recreation of the original Stanford Marshmallow experiment is predictably adorable. Longitudinal studies have shown that students who can resist eating the marshmallow are better behaved and get better grades later in life.
19. Self-control at an early age might be indicative of success later in life.
In the famous Stanford marshmallow experiment, a group of children participants were asked to wait in a room with a table full of marshmallows and cookies. If they wanted, they could have one treat now and the experiment would be over. Otherwise, if they could wait for the experimenter to return in a few minutes, they could have two treats. The children who couldn’t delay their urges—either they asked for the treat right away, or tried to sneakily eat a treat when the experimenter left—had more behavior problems, lower SAT scores, more trouble paying attention in school, and found it difficult to maintain friendships. In fact, a child who could wait 15 minutes scored 210 points higher on the SAT than children who could wait only 30 seconds.
20. People aspire to round number goals.
I tried to make this list 20 bullet points long instead of 19, and you do the same thing when trying to run 2.0 miles instead of 1.9. In Major League Baseball, players were four times as likely to end the season with a 0.300 batting average than 0.299. And when looking at over 4 million SAT scores, students who scored a 1290 were more likely to retake the test than students who scored a 1300—even though admissions offices did not statistically favor one score over the other.